The most appropriate lasers are those with wavelengths between 700 and 1400 nm, because this range offers the greatest absorption of melanin and the least interference with other pigments, such as haemoglobin.
The lasers most frequently used are:
Ruby laser: It emits 694 nm red light. In hair removal a longer pulse and lesser potency are used. Ruby laser is used occasionally for fair phototypes (I to III) with dark hair.
Alexandrite laser: Emits a wavelength of 755 nm. It penetrates deeper than the ruby laser, which means it can be used for darker phototypes (up to phototype IV). The pulse may be fixed or variable and the spot size may reach 18 mm. Some systems incorporate a scanning system that enables the treatment of wider areas. Gas, gel or cold air are used as cooling systems. One of the advantages of the alexandrite laser is that it is quite fast. Some systems require shaving of the area. Its disadvantages include not being the most appropriate for very dark phototypes (V) or for facial hair removal.
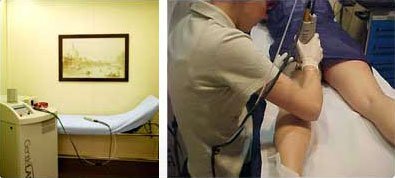
Alexandrite laser(Candela)
Diode laser: It emits a wavelength of 800-810 nm and enables the variation of pulse duration. The spot size is 9 x 9 mm. As long as the hair is dark, darker phototypes (V) can be treated without producing a lesion in the epidermis. The greater the wavelength is, the lesser absorption of melanin, requiring more energy. The cooling system consists of a sapphire in the hand piece that comes into contact with the skin. Shaving of the area is required.
The diode laser’s main advantage is that it allows the treatment of darker phototypes preserving the epidermis. Its basic drawback is that it’s a slower system due to the small spot size. It is not used for facial hair removal because of its wavelength and need of previous shaving of the area.
Neodymium:YAG laser: It emits a wavelength of 1064 nm through Q-switched pulses or long pulses. This wavelength is mildly absorbed by the pigments, which enables the treatment of all skin types. However, it is less effective. The lesser absorption of melanin requires the use of high fluencies although it can be used to treat darker phototypes without any risks. Long pulse systems emit single pulses of variable duration and the spot size measures 2 to 4 mm. Some systems require the external application of carbon particles to increase their absorption.
Intense pulsed light: It emits light with a 590 to 1200 nm wavelength. The pulses are generated by a lamp or pulsed “flash lamp”. Filters are used to determine the most appropriate spectrum according to the patient’s skin and hair type. Short filters are used (590, 615) for fair skin and fine hair. If the skin is tan and the hair is dark, longer filters are used (645, 695, 755).
Intense pulsed light is applied to the patient with a quartz guide. It enables the use of multipulses and the variation of pulse durations and the intervals between each. This makes many combinations possible and is especially useful in facial hair removal. Most systems include software that automatically selects the necessary parameters, but the doctor can modify them manually (users parameters). The cooling system consists of gel (at 4º C), which improves the light’s distribution and cools the epidermis. It is a very versatile system that requires skilled training and knowledge of the technique.