Breast augmentation is the second most requested cosmetic procedure in Spain after liposuction.
One of the most important factors of femininity is breast aesthetics. Their shape and size condition women to a great extent and thus affecting their self-esteem and confidence.
There is no such thing as the perfect breast. But when it is too small or lacks volume due to breast-feeding of important weight loss, it can be corrected easily with a breast implant.

Breast aesthetics is one of the most important factors of femininity
Breast augmentation (augmentation mamaplasty) has become one of the most popular cosmetic surgery procedures in recent years especially among younger women. It is estimated that last year alone 20,000 pairs of prostheses were implanted.
The ideal woman of the 90´s had feminine and womanly curves and having small breasts was a defect that needed to be corrected. Fortunately, the procedure is becoming less and less complex and prostheses are safer and more durable. Surgery lasts less than an hour and the patient only needs to stop normal activity for three or four days. Breast enhancement is now easier than ever, for as long as the procedure is carried out by skilled surgeons and in fully accredited clinics.
"Instituto Médico Láser has been performing augmentation mamaplasties for quite some time. Lately, though, there has been a dramatic increase in the demand of this procedure, and by younger and younger women ", explained Ignacio Sanz, plastic and cosmetic surgeon at Instituto Médico Láser. "The medical industry is constantly studying new safer and more durable prostheses".
Breast implants come in different forms, shapes and sizes; although they are all enveloped in silicon filled with saline (water) or silicon gel. The silicon gel implants are the most reliable and render excellent and very natural aesthetic results.
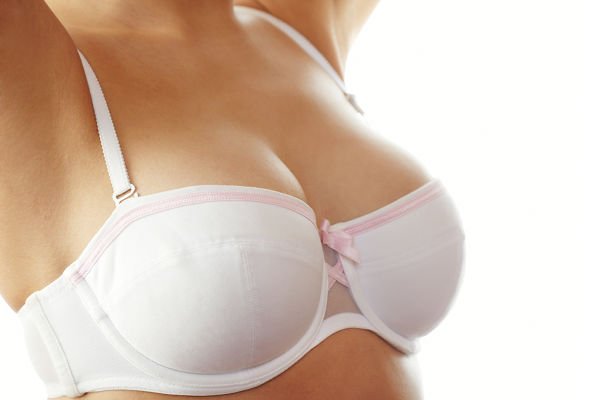
The access routes for breast implants are three: Submammary, Axillary and Areolar. Each method has its advantages and disadvantages. The final choice depends on the personal experiences of the surgeon and the physical features of the patient.
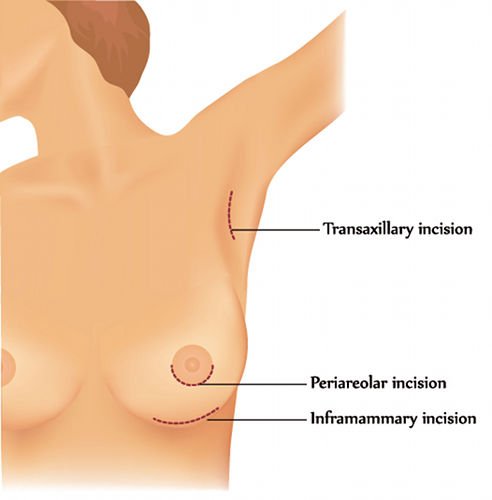
In this case, there are also various options for the placing of the breast implant and the decision should be made based on the patient’s physical features.
Breast implants have gone through an important evolution process and the earlier silicon gel implants have been substituted by cohesive gels. Cohesive gel has many advantages over the previous type of gel used. Basically, it feels more “compact”, although not necessarily harder. The advantage of cohesive gel is its greater security:
The comparison between earlier models and the newer ones can be related to that of a current car and one that is 15 years old.
Present-day implants are excellent and regardless of the brand, they all have similar features. The main differences are in the models and shapes. Each manufacturer markets an enormous selection of implants. The choice of responsibility of the surgeon, always assuring that it adapts to the patient’s thorax.
In order to obtain a natural result, it is vital to respect the natural aesthetic lines of the breast. The most important of these is the line from the collar bone to the nipple. This line must be straight given that no top bulging, causing a "ball" effect exists in nature in that area.
The shape of the implant is not important for this line to be straight (anatomical or round). What is important is that the vertical diameter of the prosthesis does not protrude or go beyond a certain point. This calculation is quite simple for an experienced surgeon and confirms that there are appropriate implants for every patient where volume and / or size have no relevance at all.
The most important factor is the diameter and if these are correctly calculated, more or less volume can be added y choosing different prosthesis models.
At present, the prostheses used are made of cohesive gel which is silicone gel, like the ones made some time ago, but with the difference that the gel has been treated to provide specific physical qualities. These qualities prevent the passage of the substance into other parts of the body should a rupture of the capsule occur. Future replacement of the prosthesis is also facilitated.

Is vital to respect the natural aesthetic lines of the breast
There are two types of cohesive gel prostheses: anatomical and round-shaped prostheses:
These implants simulate the shape of the mammary gland in the vertical position. They were originally designed as implants for mammary reconstruction. The main advantage being that they best simulate the breast shape in extremely thin patients. Their features are:
The features of round implants are:

The results of an augmentation mammoplasty are completely natural and aesthetically perfect if the size and final volume follow those appropriate to the patient’s thorax and physical features.
1. Can a mammography be performed after a breast augmentation?
Yes. The physician should be informed that the patient has breast implants. Nevertheless, mammary ultrasounds are more advisable in these cases.
2. Is there a risk of cancer or breast disease?
Absolutely not. Every study ever carried out has shown no risk at all.
3. Can I breast-feed?
Yes. The implant does not affect the normal functioning of the mammary gland in any way whatsoever. In the event of pregnancy and breast-feeding, the aesthetic changes are those typical to any woman and have no relation with the prosthesis.
4. Is there a loss of sensibility?
No. There may be alterations in sensibility in the first few months, but these can increase or decrease but these are completely transitory since they are due to post-operative inflammation.
5. Will it be noticeable?
Yes. Those closest to you will notice the change, but the important point is that strangers will not notice that those beautiful breasts are the result of an operation. It must be natural and integrate perfectly with each patient's physical structure with the ability to move.
6. Do implants explode?
Absolutely not. It is advisable during the first month to avoid flights of over 6 hours since the cabin pressure can increase inflammation. Implants have been tested at NASA laboratories and they do not explode.
7. Should they be periodically replaced?
No. Mammary implants should be checked once a year but they do not need replacing unless a problem is detected. Manufacturers issue guarantees that cover a certain number of years, but this does not mean that they require replacing.
Breast prostheses can be inserted behind the gland (retroglandular) or behind the pectoral muscle (retropectoral). The advantage of positioning the prosthesis behind the muscle is that it looks more natural, as the pectoral muscle hides giving it shape. It is the best option in patients with small breasts.
The type of prosthesis can be: high profile, when the breast needs correction; low profile, when the breast cup is sufficiently big; and anatomical or tear-shaped.
In some cases, it can be combined with a reduction of the areolar size.
The approach route can be periareolar, through the submammary furrow or via the axilla.
For personalised information of mamaplasty, contact IML now and we will give you a free informative consultation with one of our surgeons experts.